
Managing yourself- Starting with your brain
Conflict is, by its very nature, stressful. Being able to get your own brain under control during conflict comes down to you being able to manage yourself productively under stress. Below we will explore a few ways to get your brain under control during times of conflict. But first, let’s take a look at what stress really is.
What Is the Cost of Social Stress?
Stress is a frequent experience for many of us. Stress – which can be broadly defined as a threat or challenge to our well-being – can result from everyday events like a course exam or a more extreme event, such as a natural disaster. When faced with a stressor, sympathetic nervous system activity increases in order to prepare our body to respond to the challenge. This produces what Selye (1950) called a fight or flight response. The release of hormones, which act as messengers from one part of an organism (e.g., a cell or gland) to another part of the organism.
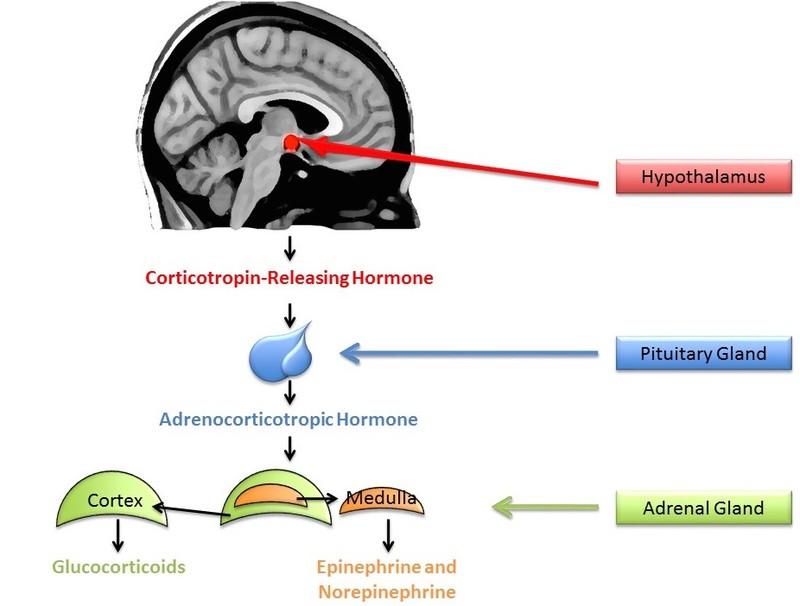
A small amount of stress can actually help us stay alert and active. In comparison, sustained stressors, or chronic stress, detrimentally affects our health and impairs performance (Al’absi, Hugdahl, & Lovallo, 2002; Black, 2002; Lazarus, 1974). This happens through the chronic secretion of stress-related hormones (e.g., Davidson, Pizzagalli, Nitschke, & Putnam, 2002; Dickerson, Gable, Irwin, Aziz, & Kemeny, 2009). In particular, stress activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HAP) axis to release cortisol (see Figure 5 for a discussion). Chronic stress, by way of increases in cortisol, impairs attention, memory, and self-control (Arnsten, 2009). Cortisol levels can be measured non-invasively in bodily fluids, including blood and saliva. Researchers often collect a cortisol sample before and after a potentially stressful task. In one common collection method, subjects place polymer swabs under their tongue for 1 to 2 minutes to soak up saliva. The saliva samples are then stored and analyzed later to determine the level of cortisol present at each time point.
Whereas early stress researchers studied the effects of physical stressors like loud noises, social neuroscientists have been instrumental in studying how our interactions with other people can cause stress. This question has been addressed through neuroendocrinology, or the study of how the brain and hormones act in concert to coordinate the physiology of the body. One contribution of this work has been in understanding the conditions under which other people can cause stress. In one study, Dickerson, Mycek, and Zaldivar (2008) asked undergraduates to deliver a speech either alone or to two other people. When the students gave the speech in front of others, there was a marked increase in cortisol compared with when they were asked to give a speech alone. This suggests that like chronic physical stress, everyday social stressors, such as having your performance judged by others, induces a stress response. Interestingly, simply giving a speech in the same room with someone who is doing something else did not induce a stress response. This suggests that the mere presence of others is not stressful, but rather it is the potential for them to judge us that induces stress.
Worrying about what other people think of us is not the only source of social stress in our lives. Other research has shown that interacting with people who belong to different social groups than us – what social psychologists call outgroup members – can increase physiological stress responses. For example, cardiovascular responses associated with stress like contractility of the heart ventricles and the amount of blood pumped by the heart (what is called cardiac output) are increased when interacting with outgroup as compared with ingroup members (i.e., people who belong to the same social group we do) (Mendes, Balscovish, Likel, & Hunter, 2002). This stress may derive from the expectation that interactions with dissimilar others will be uncomfortable (Stephan & Stephan, 1985) or concern about being judged as unfriendly and prejudiced if the interaction goes poorly (Plant & Devine, 2003).
The research just reviewed shows that events in our social lives can be stressful, but are social interactions always bad for us? No. In fact, while others can be the source of much stress, they are also a major buffer against stress. Research on social support shows that relying on a network of individuals in tough times gives us tools for dealing with stress and can ward off loneliness (Cacioppo & Patrick, 2008). For instance, people who report greater social support show a smaller increase in cortisol when performing a speech in front of two evaluators (Eisenberger, Tayler, Gable, Hilmert, & Lieberman, 2007).
What determines whether others will increase or decrease stress? What matters is the context of the social interaction. When it has potential to reflect badly on ourself, social interaction can be stressful, but when it provides support and comfort, social interaction can protect us from the negative effects of stress. Using neuroendocrinology by measuring hormonal changes in the body has helped researchers better understand how social factors impact our body and ultimately our health.
McGonigal, K. (2013 ). How to Make Stress Your Friend. Ted Talk. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RcGyVTAoXEU&t=413s
Take a Deep Breath
One simple, and often over looked strategy for managing stress, and specifically getting our own brain under control, is to simply focus on our breathing. Take a deep breath sends a message to your brain to calm and slow down.
Check out Stacey Schuerman’s Ted Talk, Breath– five minutes can change your life to practice how to use your breath to calm down and get your brain under control.
Take a Break
If you find yourself overwhelmed, triggered, and actively in conflict. Don’t be afraid to take a break. Taking a break when you need one, is a great place to be assertive and create the boundaries that you need in your life. Sometimes you only need a break for 5 minutes to calm down, get your brain under control, and re-engage in the conflict in a more productive way. Other times you may need an hour break.
When you need to take a break in the middle of a conversation of a conflict, don’t forget to use productive framing and I-Statements to help the other person understand what you need. Here are two examples:
“I know we are in the middle of this conversation, but right now I can’t get my thoughts together. I need to take a break. I’m going to take a walk for 5-10 minutes and then I will come back.”
“I’m not the best version of myself right now, I feel really overwhelmed. I care about this conversation, and you, enough to know I need to get my thoughts together. I need a day or two to process all this new information. Can we set up a time to pick this conversation back up?”

